Major Research Projects
Funding
We are funded by ERC, MRC, BBSRC, EMBO, British Council, Newton Bhabha, Erasmus and Wellcome Trust.
Overview
The research in the group has undertaken genome wide functional studies using rodent malaria model P. berghei to understand parasite developmental biology and the crucial novel molecules that are part of the signalling cascades, cell division, polarity during parasite development.
Major projects undertaken in the group are:
1. Understanding molecular mechanism regulating unusual cell division and cell polarity in malaria parasite
Cell division and proliferation require a process of chromosome replication and segregation that ensure that the two daughter cells obtain identical copies of the genome. Malaria parasites representing divergent eukaryote divide and proliferate within host cells in a unique way that is different from that of many model eukaryotes. Many of the regulators as part of reversible phosphorylation (kinases and phosphatases) and motor proteins required for progression through cell development and polarity, mitosis and meiotic division are either diverged or missing from Plasmodium. Most of our studies are also focussed on understanding the cell biology of the sexual and sporogony stages of parasite development occurring within mosquito vector. These are difficult stages to study in many apicomplexan parasites, including malaria parasites. Our recent research has given us an important insight to understand the mechanism and function of some of these molecules as described below:
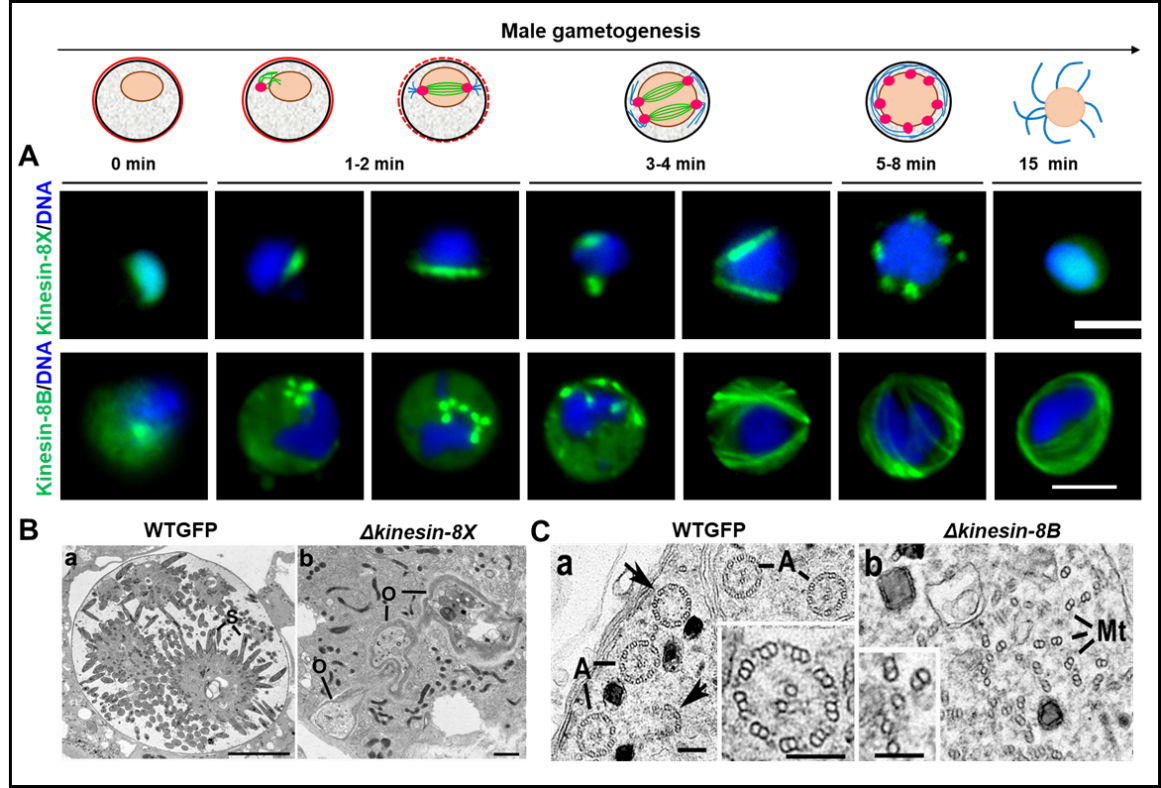
1A. Kinesins - Molecular motors in cell division
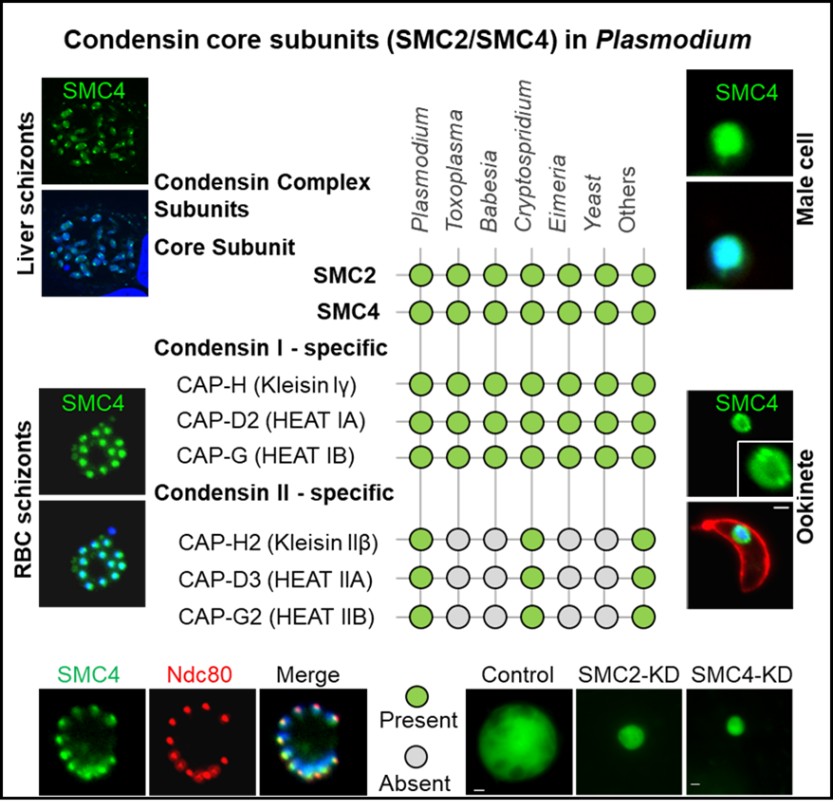
1B. Condensin core subunits - SMC2/SMC4 in Plasmodium cell division
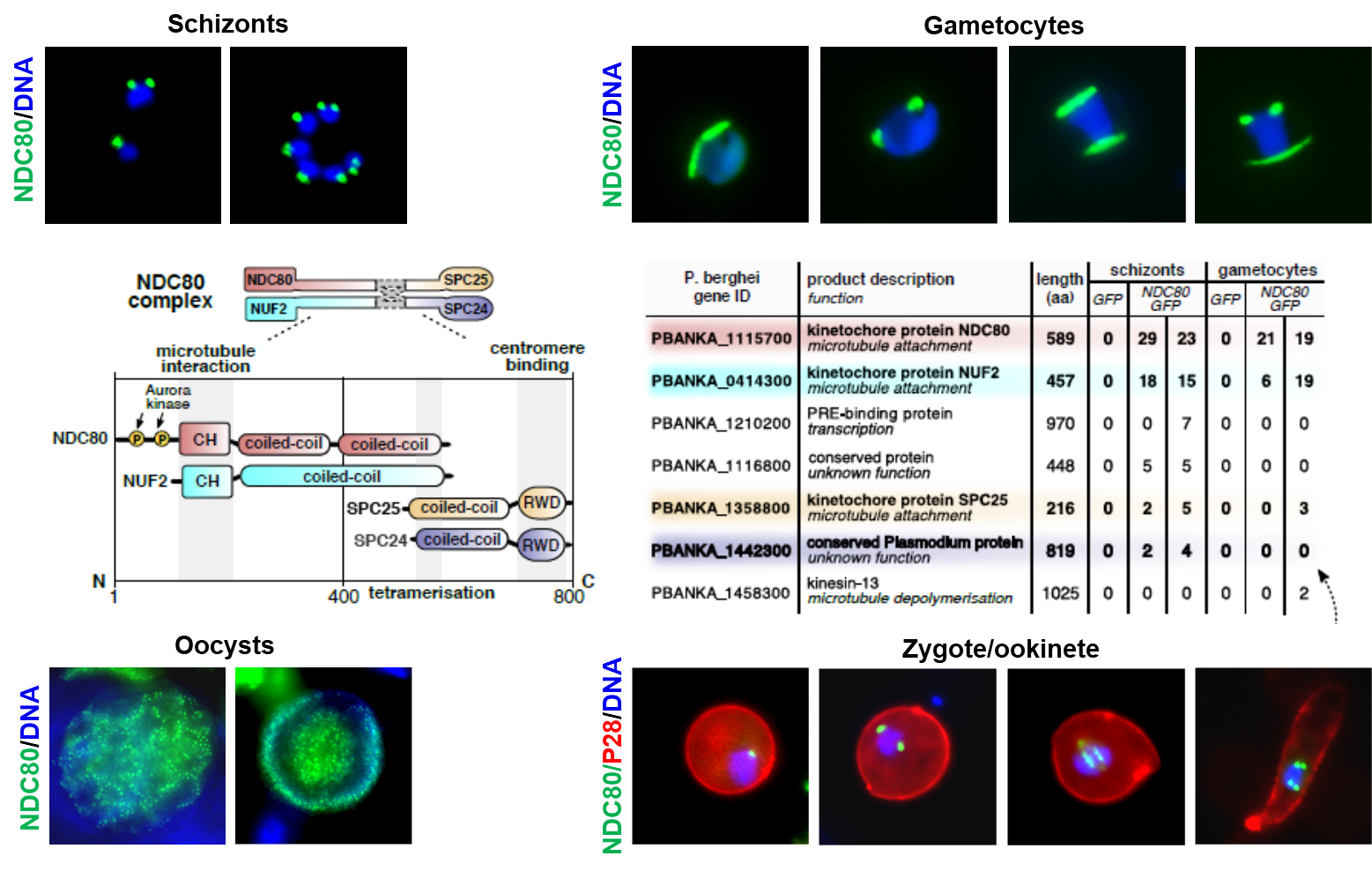
1C. Kinetochore complex – Plasmodium NDC80 dynamics in chromosome segregation during proliferative stages
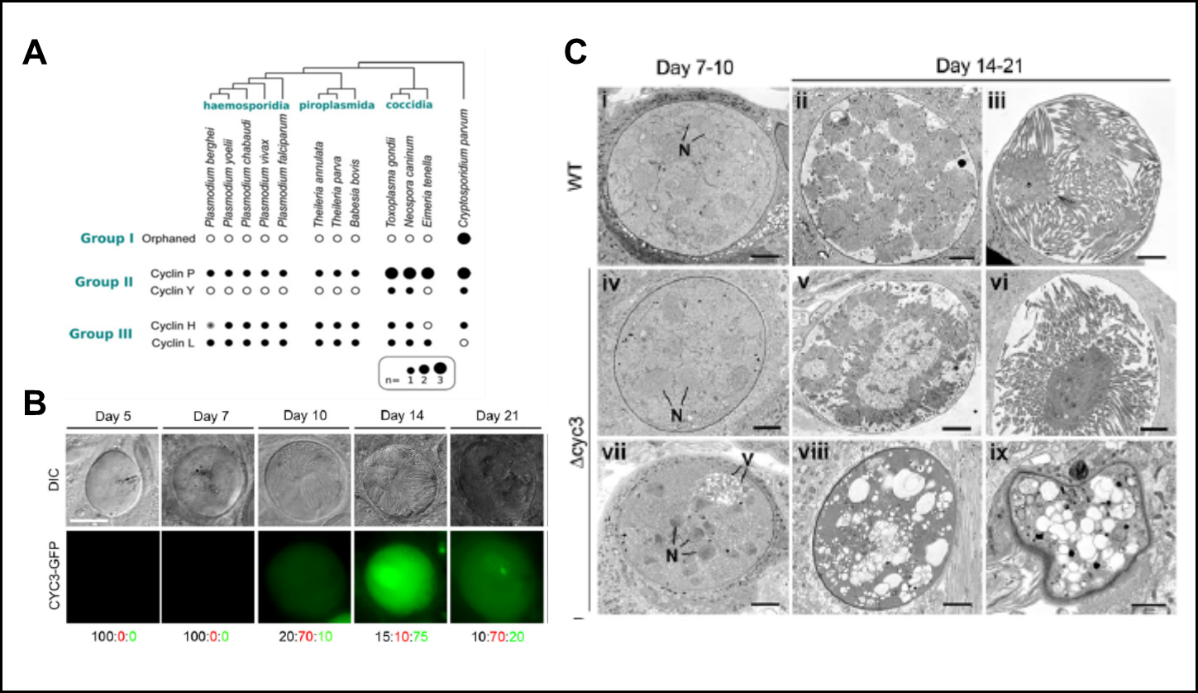
1D. Cyclins - Cyclin3 in Plasmodium
2. Reversible phoshorylation and parasite development in malaria parasite
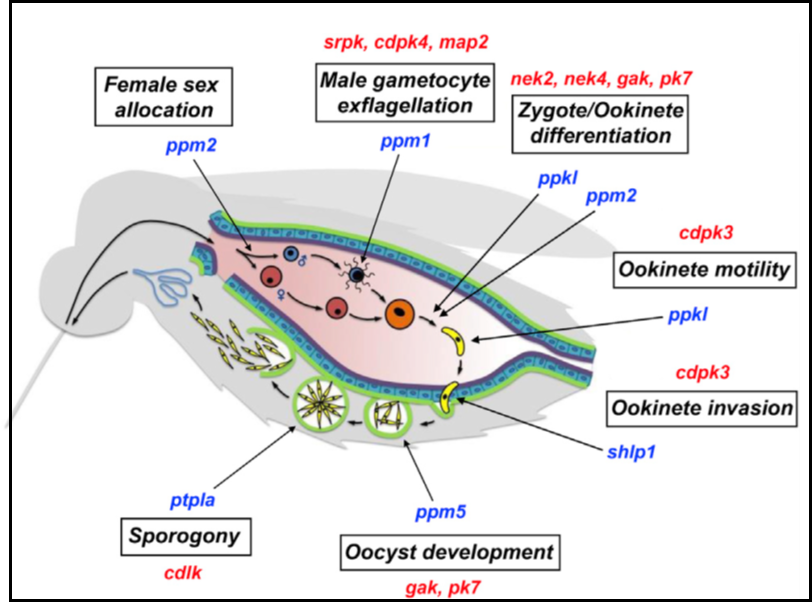
2A. Kinases and Phosphatases functional screen
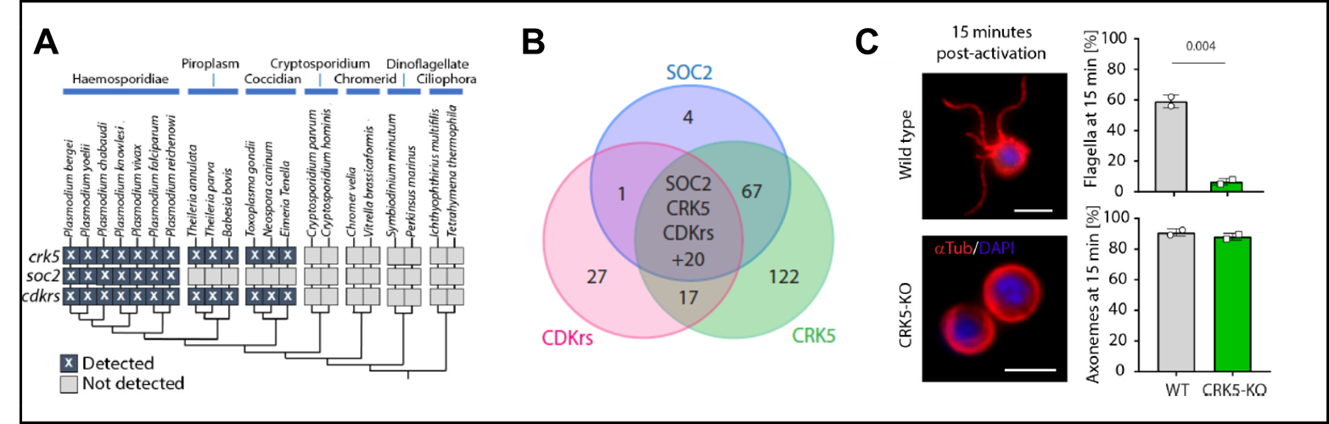
2B. Plasmodium specific Cyclin dependent protein kinase CRK5-cyclin complex and function during male gametogenesis
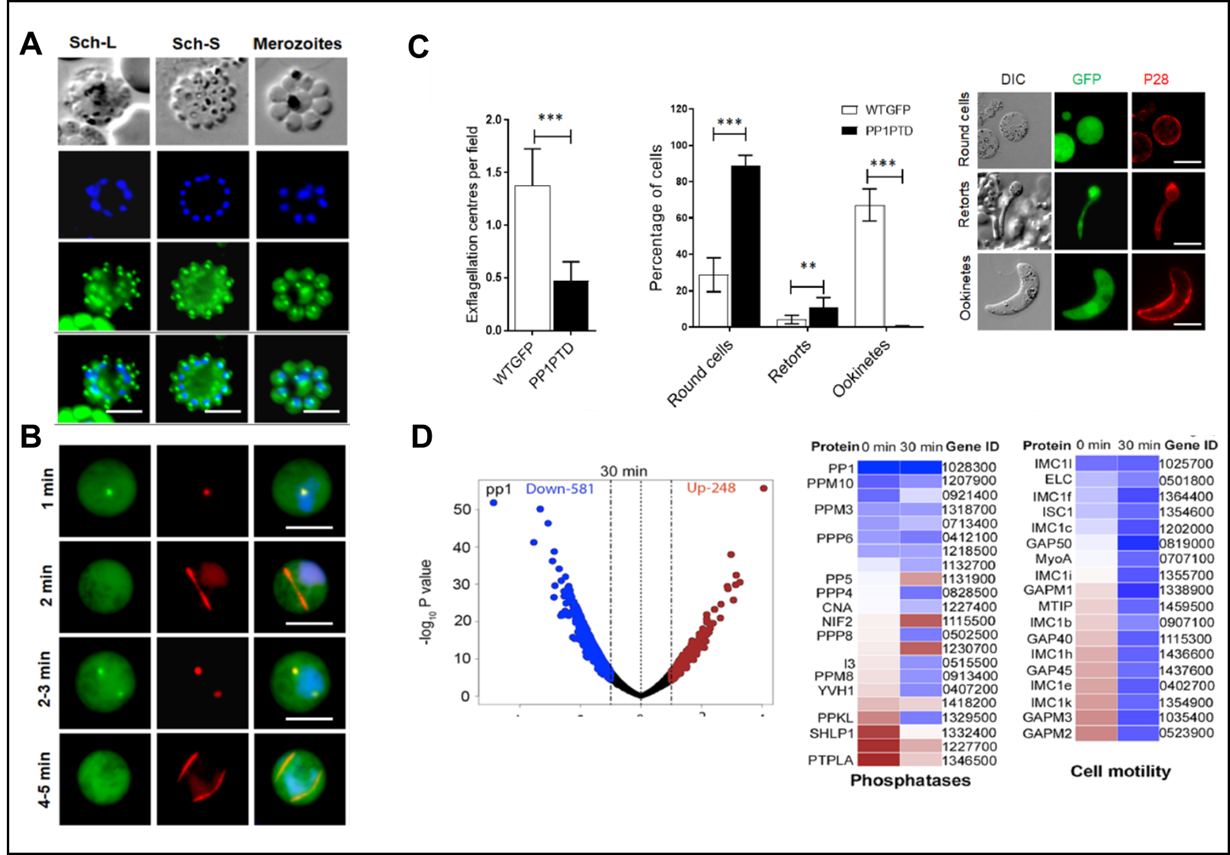
2C. Phosphatase PP1 in male gametogenesis and ookinete formation
3. Cell polarity during motile and invasive stages in Plasmodium
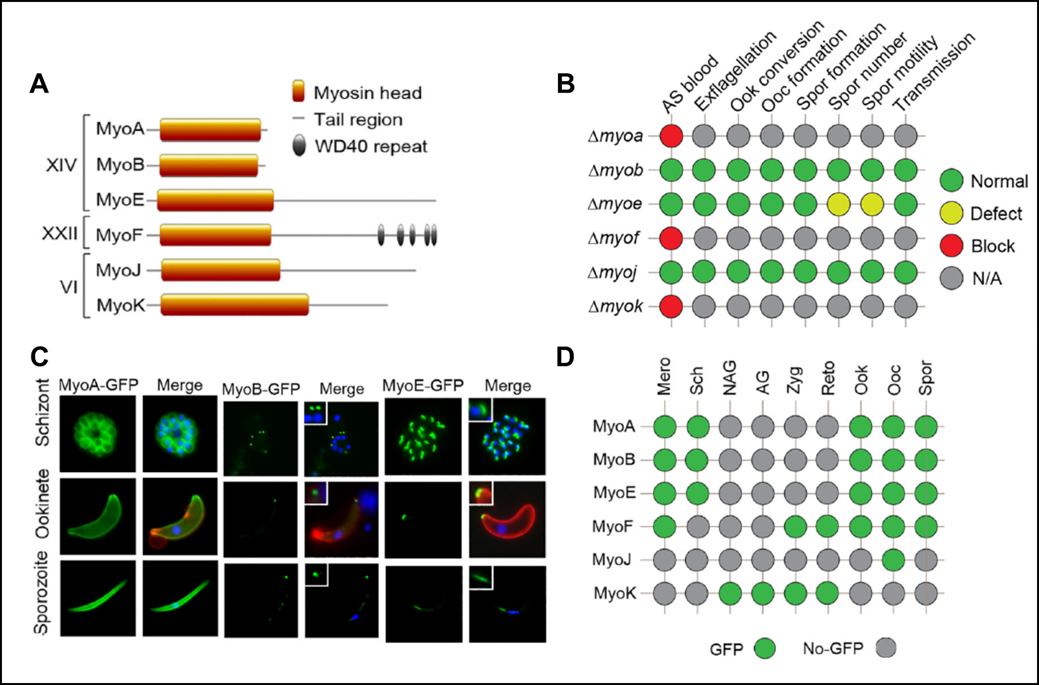
3A. Myosin gene family
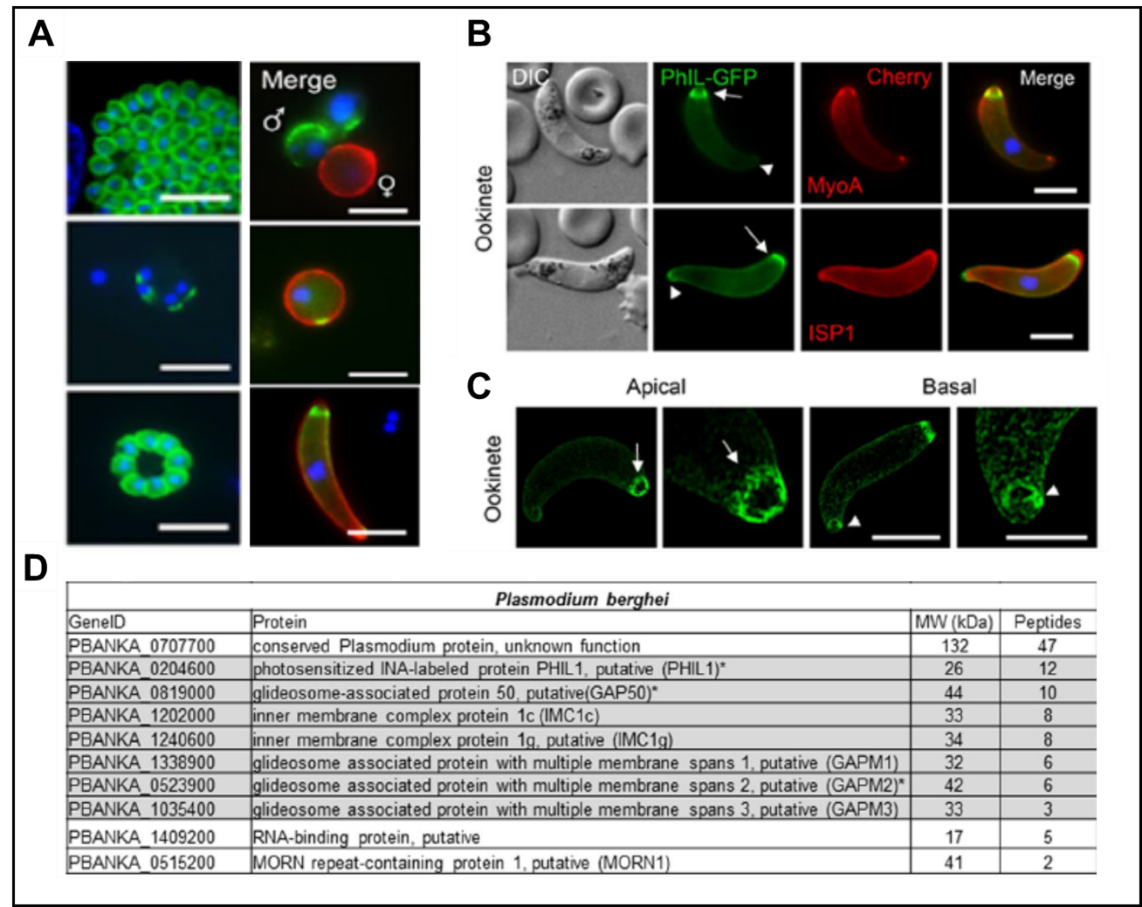
3B. Phil1 is novel complex present during invasive stages